Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate whether it is levorotatory or racemic.
Identification—
It meets the requirements of the test for
Lactate  191
191
.
Specific rotation  781A
781A :
:
between
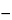
0.05
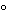
and +0.05
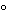
, for racemic Lactic Acid.
Readily carbonizable substances—
Rinse a test tube with
sulfuric acid TS, and allow to drain for 10 minutes. Add 5 mL of
sulfuric acid TS to the test tube, carefully overlay it with 5 mL of Lactic Acid, and maintain the tube at a temperature of 15
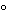
: no dark color develops at the interface of the two acids within 15 minutes.
Sugars—
To 10 mL of hot alkaline cupric tartrate TS add 5 drops of Lactic Acid: no red precipitate is formed.
Chloride—
To 10 mL of a solution (1 in 100) acidified with nitric acid add a few drops of
silver nitrate TS: no opalescence is produced immediately.
Sulfate—
To 10 mL of a solution (1 in 100) add 2 drops of hydrochloric acid and 1 mL of
barium chloride TS: no turbidity is produced.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
:
0.001%.
Limit of citric, oxalic, phosphoric, or tartaric acid—
To 10 mL of a solution (1 in 10) add 40 mL of
calcium hydroxide TS, and boil for 2 minutes: no turbidity is produced.
Assay—
To about 2.5 mL of Lactic Acid, accurately weighed in a tared 250-mL flask, add 50.0 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide VS, and boil the mixture for 20 minutes. Add
phenolphthalein TS, and titrate the excess alkali in the hot solution with 1 N sulfuric acid VS. Perform a blank determination (see
Residual Titrations under
Titrimetry  541
541
). Each mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 90.08 mg of C
3H
6O
3.
Auxiliary Information—
Staff Liaison :
Lawrence Evans, III, Ph.D., Scientist
Expert Committee : (DSN05) Dietary Supplements - Non-Botanicals
USP29–NF24 Page 1223
Pharmacopeial Forum : Volume No. 28(6) Page 1817
Phone Number : 1-301-816-8389

