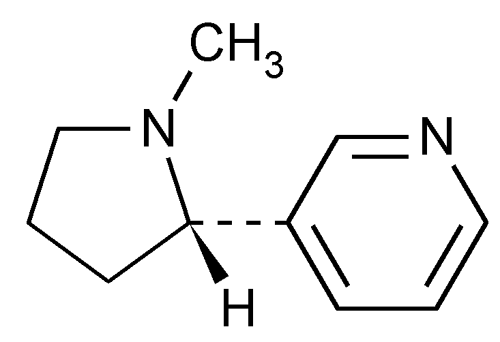
Nicotine
» Nicotine contains not less than 99.0 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of C10H14N2, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Store under nitrogen in well-closed containers below 25 , protected from light and moisture.
, protected from light and moisture.
Identification,
Ultraviolet Absorption  197U
197U —
—
Solutions—
Prepare a solution of Nicotine in water having a concentration of about 1 mg per mL. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with 0.1 N hydrochloric acid to volume, and mix to obtain the test solution. Transfer an amount of USP Nicotine Bitartrate Dihydrate RS, equivalent to about 50 mg of nicotine, to a 25-mL glass-stoppered tube. Add 5 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide, 2 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide, and 20 mL of n-hexane. Shake for 5 minutes, allow the phases to separate, transfer the upper n-hexane layer to a vial, and evaporate with a stream of nitrogen gas. [note—Avoid excessive drying to prevent loss of nicotine.] Dissolve the residue of the nicotine so obtained in water to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 1 mg per mL. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution with 0.1 N hydrochloric acid to 50.0 mL, and mix to obtain the Standard solution.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 0.5%.
:
not more than 0.5%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
not more than 0.002%.
:
not more than 0.002%.
Chromatographic purity—
Test solution—
Dissolve about 0.13 g of Nicotine, accurately weighed, in dichloromethane, dilute with dichloromethane to 25.0 mL, and mix.
Reference solutions—
Dilute accurately measured volumes of the Test solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with dichloromethane to obtain Reference solution A and Reference solution B having concentrations of about 26 µg per mL and 52 µg per mL, respectively.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector maintained at 270
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector maintained at 270 and a 0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica column bonded with a 1.5-µm layer of phase G1. Helium is used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 20 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 50
and a 0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica column bonded with a 1.5-µm layer of phase G1. Helium is used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of 20 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 50 for 6 seconds, then programmed to rise from 50
for 6 seconds, then programmed to rise from 50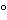 to 250
to 250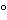 at 6
at 6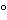 per minute, and finally held isothermally at 250
per minute, and finally held isothermally at 250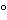 for 3 minutes.
for 3 minutes.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 1 µL) of the Test solution, Reference solution A, and Reference solution B into the chromatograph, and allow the Test solution to elute for not less than 2.5 times the retention time of nicotine. Record the chromatograms, and measure all of the peak responses. The sum of the peak responses, excluding that of nicotine, from the Test solution is not more than that of the nicotine response from Reference solution B (1.0%), and no single peak response is greater than that of the nicotine response from Reference solution A (0.5%).
Assay—
Dissolve about 60 mg of Nicotine, accurately weighed, in 40 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically (see Titrimetry  541
541 ). Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 8.11 mg of C10H14N2.
). Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 8.11 mg of C10H14N2.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8330 |
(MDPP05) Monograph Development-Psychiatrics and Psychoactives |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 3079
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 28(5) Page 1420
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.