 231
231 HEAVY METALS
HEAVY METALS
This test is provided to demonstrate that the content of metallic impurities that are colored by sulfide ion, under the specified test conditions, does not exceed the
Heavy metals limit specified in the individual monograph in percentage (by weight) of lead in the test substance, as determined by concomitant visual comparison (see
Visual Comparison in the section
Procedure under
Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851
) with a control prepared from a
Standard Lead Solution. [NOTE—Substances that typically will respond to this test are lead, mercury, bismuth, arsenic, antimony, tin, cadmium, silver, copper, and molybdenum.
]
Determine the amount of heavy metals by Method I, unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph. Method I is used for substances that yield clear, colorless preparations under the specified test conditions. Method II is used for substances that do not yield clear, colorless preparations under the test conditions specified for Method I, or for substances that, by virtue of their complex nature, interfere with the precipitation of metals by sulfide ion, or for fixed and volatile oils. Method III, a wet-digestion method, is used only in those cases where neither Method I nor Method II can be used.
Special Reagents
Lead Nitrate Stock Solution—
Dissolve 159.8 mg of lead nitrate in 100 mL of water to which has been added 1 mL of nitric acid, then dilute with water to 1000 mL. Prepare and store this solution in glass containers free from soluble lead salts.
Standard Lead Solution—
On the day of use, dilute 10.0 mL of Lead Nitrate Stock Solution with water to 100.0 mL. Each mL of Standard Lead Solution contains the equivalent of 10 µg of lead. A comparison solution prepared on the basis of 100 µL of Standard Lead Solution per g of substance being tested contains the equivalent of 1 part of lead per million parts of substance being tested.
Method I
pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer—
Dissolve 25.0 g of ammonium acetate in 25 mL of water, and add 38.0 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid. Adjust, if necessary, with 6 N ammonium hydroxide or 6 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 3.5, dilute with water to 100 mL, and mix.
Standard Preparation—
Into a 50-mL color-comparison tube pipet 2 mL of Standard Lead Solution (20 µg of Pb), and dilute with water to 25 mL. Using a pH meter or short-range pH indicator paper as external indicator, adjust with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
Test Preparation—
Into a 50-mL color-comparison tube place 25 mL of the solution prepared for the test as directed in the individual monograph; or, using the designated volume of acid where specified in the individual monograph, dissolve in and dilute with water to 25 mL the quantity, in g, of the substance to be tested, as calculated by the formula:
2.0/(1000L),
in which
L is the
Heavy metals limit, as a percentage. Using a pH meter or short-range pH indicator paper as external indicator, adjust with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
Monitor Preparation—
Into a third 50-mL color-comparison tube place 25 mL of a solution prepared as directed for Test Preparation, and add 2.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution. Using a pH meter or short-range pH indicator paper as external indicator, adjust with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
Procedure—
To each of the three tubes containing the
Standard Preparation, the
Test Preparation, and the
Monitor Preparation, add 2 mL of
pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, then add 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS, dilute with water to 50 mL, mix, allow to stand for 2 minutes, and view downward over a white surface
*: the color of the solution from the
Test Preparation is not darker than that of the solution from the
Standard Preparation, and the color of the solution from the
Monitor Preparation is equal to or darker than that of the solution from the
Standard Preparation. [NOTE—If the color of the
Monitor Preparation is lighter than that of the
Standard Preparation, use
Method II instead of
Method I for the substance being tested.
]
Method II
NOTE—This method does not recover mercury.
pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer—
Prepare as directed under Method I.
Standard Preparation—
Pipet 4 mL of the Standard Lead Solution into a suitable test tube, and add 10 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid.
Test Preparation—
Use a quantity, in g, of the substance to be tested as calculated by the formula:
4.0/(1000L),
in which
L is the
Heavy metals limit, as a percentage. Transfer the weighed quantity of the substance to a suitable crucible, add sufficient sulfuric acid to wet the substance, and carefully ignite at a low temperature until thoroughly charred. (The crucible may be loosely covered with a suitable lid during the charring.) Add to the carbonized mass 2 mL of nitric acid and 5 drops of sulfuric acid, and heat cautiously until white fumes no longer are evolved. Ignite, preferably in a muffle furnace, at 500
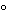
to 600
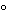
, until the carbon is completely burned off (no longer than 2 hours). If carbon remains, allow the residue to cool, add a few drops of sulfuric acid, evaporate, and ignite again. Cool, add 5 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, cover, and digest on a steam bath for 10 minutes. Cool, and quantitatively transfer the solution to a test tube. Rinse the crucible with a second 5-mL portion of 6 N hydrochloric acid, and transfer the rinsing to the test tube.
Monitor Preparation—
Pipet 4 mL of the Standard Lead Solution into a crucible identical to that used for the Test Preparation and containing a quantity of the substance under test that is equal to 10% of the amount required for the Test Preparation. Evaporate on a steam bath to dryness. Ignite at the same time, in the same muffle furnace, and under the same conditions used for the Test Preparation. Cool, add 5 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, cover, and digest on a steam bath for 10 minutes. Cool, and quantitatively transfer to a test tube. Rinse the crucible with a second 5-mL portion of 6 N hydrochloric acid, and transfer the rinsing to the test tube.
Procedure—
Adjust the solution in each of the tubes containing the Standard Preparation, the Test Preparation, and the Monitor Preparation with ammonium hydroxide, added cautiously and dropwise, to a pH of 9. Cool, and adjust with glacial acetic acid, added dropwise, to a pH of 8, then add 0.5 mL in excess. Using a pH meter or short-range pH indicator paper as external indicator, check the pH, and adjust, if necessary, with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0. Filter, if necessary, washing the filter with a few mL of water, into a 50-mL color-comparison tube, and then dilute with water to 40 mL. Add 2 mL of pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, then add 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS, dilute with water to 50 mL, mix, allow to stand for 2 minutes, and view downward over a white surface*: the color of the solution from the Test Preparation is not darker than that of the solution from the Standard Preparation, and the color of the solution from the Monitor Preparation is equal to or darker than that of the solution from the Standard Preparation. [NOTE—If the color of the solution from the Monitor Preparation is lighter than that of the solution from the Standard Preparation, proceed as directed for Method III for the substance being tested.]
Method III
pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer—
Prepare as directed under Method I.
Standard Preparation—
Transfer a mixture of 8 mL of sulfuric acid and 10 mL of nitric acid to a clean, dry, 100-mL Kjeldahl flask, and add a further volume of nitric acid equal to the incremental volume of nitric acid added to the Test Preparation. Heat the solution to the production of dense, white fumes; cool; cautiously add 10 mL of water; and, if hydrogen peroxide was used in treating the Test Preparation, add a volume of 30 percent hydrogen peroxide equal to that used for the substance being tested. Boil gently to the production of dense, white fumes. Again cool, cautiously add 5 mL of water, mix, and boil gently to the production of dense, white fumes and to a volume of 2 to 3 mL. Cool, dilute cautiously with a few mL of water, add 2.0 mL of Standard Lead Solution (20 µg of Pb), and mix. Transfer to a 50-mL color-comparison tube, rinse the flask with water, adding the rinsing to the tube until the volume is 25 mL, and mix.
Test Preparation—
Unless otherwise indicated in the individual monograph, use a quantity, in g, of the substance to be tested as calculated by the formula:
2.0/(1000L),
in which
L is the
Heavy metals limit, as a percentage.
If the substance is a solid—
Transfer the weighed quantity of the test substance to a clean, dry, 100-mL Kjeldahl flask.
[NOTE—A 300-mL flask may be used if the reaction foams excessively.
] Clamp the flask at an angle of 45
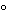
, and add a sufficient quantity of a mixture of 8 mL of sulfuric acid and 10 mL of nitric acid to moisten the substance thoroughly. Warm gently until the reaction commences, allow the reaction to subside, and add portions of the same acid mixture, heating after each addition, until a total of 18 mL of the acid mixture has been added. Increase the amount of heat, and boil gently until the solution darkens. Cool, add 2 mL of nitric acid, and heat again until the solution darkens. Continue the heating, followed by addition of nitric acid until no further darkening occurs, then heat strongly to the production of dense, white fumes. Cool, cautiously add 5 mL of water, boil gently to the production of dense, white fumes, and continue heating until the volume is reduced to a few mL. Cool, cautiously add 5 mL of water, and examine the color of the solution. If the color is yellow, cautiously add 1 mL of 30 percent hydrogen peroxide, and again evaporate to the production of dense, white fumes and a volume of 2 to 3 mL. If the solution is still yellow, repeat the addition of 5 mL of water and the peroxide treatment. Cool, dilute cautiously with a few mL of water, and rinse into a 50-mL color-comparison tube, taking care that the combined volume does not exceed 25 mL.
If the substance is a liquid—
Transfer the weighed quantity of the test substance to a clean, dry, 100-mL Kjeldahl flask.
[NOTE—A 300-mL flask may be used if the reaction foams excessively.
] Clamp the flask at an angle of 45
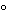
, and cautiously add a few mL of a mixture of 8 mL of sulfuric acid and 10 mL of nitric acid. Warm gently until the reaction commences, allow the reaction to subside, and proceed as directed for
If the substance is a solid, beginning with “add portions of the same acid mixture.”
Monitor Preparation—
Proceed with the digestion, using the same amount of sample and the same procedure as directed in the subsection If the substance is a solid in the section Test Preparation, until the step “Cool, dilute cautiously with a few mL of water.” Add 2.0 mL of Lead Standard Solution (20 µg of lead), and mix. Transfer to a 50-mL color comparison tube, rinse the flask with water, adding the rinsing to the tube until the volume is 25 mL, and mix.
Procedure—
Treat the
Test Preparation, the
Standard Preparation, and the
Monitor Preparation as follows. Using a pH meter or short-range pH indicator paper as external indicator, adjust the solution to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0 with ammonium hydroxide (a dilute ammonia solution may be used, if desired, as the specified range is approached), dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
To each tube add 2 mL of
pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, then add 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS, dilute with water to 50 mL, mix, allow to stand for 2 minutes, and view downward over a white surface
*: the color of the
Test Preparation is not darker than that of the
Standard Preparation, and the color of the
Monitor Preparation is equal to or darker than that of the
Standard Preparation.
*
In those countries or jurisdictions where thioacetamide cannot be used, add 10 mL of freshly prepared
hydrogen sulfide TS to each of the tubes, mix, allow to stand for 5 minutes, and view downward over a white surface.

