Use membrane filters having a nominal pore size not greater than 0.45 µm whose effectiveness to retain microorganisms has been established. Cellulose nitrate filters, for example, are used for aqueous, oily, and weakly alcoholic solutions; and cellulose acetate filters, for example, are used for strongly alcoholic solutions. Specially adapted filters may be needed for certain products (e.g., for antibiotics).
The technique described below assumes that membranes about 50 mm in diameter will be used. If filters of a different diameter are used, the volumes of the dilutions and the washings should be adjusted accordingly. The filtration apparatus and membrane are sterilized by appropriate means. The apparatus is designed so that the solution to be examined can be introduced and filtered under aseptic conditions: it permits the aseptic removal of the membrane for transfer to the medium, or it is suitable for carrying out the incubation after adding the medium to the apparatus itself.
SOLIDS FOR INJECTION OTHER THAN ANTIBIOTICS
Constitute the test articles as directed on the label, and proceed as directed for Aqueous Solutions or Oils and Oily Solutions, whichever applies. [NOTE—If necessary, excess diluent can be added to aid in the constitution and filtration of the constituted test article.]
ANTIBIOTIC SOLIDS FOR INJECTION
Pharmacy Bulk Packages, < 5 g—
From each of 20 containers, aseptically transfer about 300 mg of solids, into a sterile 500-mL conical flask, dissolve in about 200 mL of Fluid A (see Diluting and Rinsing Fluids for Membrane Filtration), and mix; or constitute, as directed in the labeling, each of 20 containers and transfer a quantity of liquid or suspension, equivalent to about 300 mg of solids, into a sterile 500-mL conical flask, dissolve in about 200 mL of Fluid A, and mix. Proceed as directed for Aqueous Solutions or Oils and Oily Solutions, whichever applies.
Pharmacy Bulk Packages, 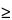 5 g—
5 g—
From each of 6 containers, aseptically transfer about 1 g of solids into a sterile 500-mL conical flask, dissolve in about 200 mL of
Fluid A, and mix; or constitute, as directed in the labeling, each of 6 containers and transfer a quantity of liquid, equivalent to about 1 g of solids, into a sterile 500-mL conical flask, dissolve in about 200 mL of
Fluid A, and mix. Proceed as directed for
Aqueous Solutions.
DEVICES WITH PATHWAYS LABELED STERILE
Aseptically pass not less than 10 pathway volumes of Fluid D through each device tested. Collect the fluids in an appropriate sterile vessel, and proceed as directed for Aqueous Solutions or Oils and Oily Solutions, whichever applies.
In the case of sterile, empty syringes, draw sterile diluent into the barrel through the sterile needle, if attached, or through a sterile needle attached for the purpose of the test, and express the contents into a sterile pooling vessel. Proceed as directed above.