Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Identification—
Determine by pyrolysis gas chromatography, using the following procedure.
Standard preparation—
Transfer an appropriate amount of
USP Colestipol Hydrochloride RS into the probe. If necessary to keep the colestipol hydrochloride in the probe, mix 4 parts with 1 part of
n-eicosane. Grind in a mortar with chloroform until the colestipol hydrochloride is uniformly coated with the
n-eicosane. This preparation is stable indefinitely but may require wetting with a small amount of chloroform before each use.
Test preparation—
Proceed as directed under Standard preparation, using an appropriate amount of the test specimen.
Chromatographic system
(see
Chromatography  621
621
)—The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 3-mm × 180-cm column packed with 80- to 100-mesh support S1A which has been coated with 0.25% potassium hydroxide and 5% phase G16. The carrier gas is helium at a flow rate of about 60 mL per minute. Maintain the detector and column temperatures at about 270
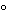
and about 85
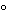
, respectively. The pyrolysis unit is capable of reaching 1100
when equipped with a platinum probe, and pyrolysis time is not less than 10 seconds.
Procedure—
Install the pyrolysis unit on the chromatograph, and position the probe so that it is just above but not touching the column packing. Set the pyrolysis temperature to about 1100
.
Separately pyrolyze the Standard preparation and the Test preparation. After the completion of each pyrolysis cycle, remove and clean the probe. The pyrogram of the Test preparation corresponds to that of the Standard preparation obtained the same day.
pH  791
791 —
—
Prepare a 10% (w/w) suspension of it in deionized water in a clean vial. Insert the stopper, shake at approximately 10-minute intervals for 1 hour, and centrifuge. Transfer a portion of the clear supernatant to a suitable container, and record the pH as soon as the reading has stabilized: the pH is between 6.0 and 7.5.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
—
Dry it in vacuum at a pressure of about 5 mm of mercury at 75
for 16 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
:
not more than 0.002%.
Content of chloride—
Test preparation—
Using about 20 mg of Colestipol Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, proceed as directed under
Oxygen Flask Combustion  471
471
, 10 mL of 0.05 N sodium hydroxide being used as the absorbing liquid. Do not allow the paper specimen wrapper to come in contact with the liquid, and ignite the paper with an IR igniter. After combustion is complete, shake the flask vigorously, and allow to stand, with frequent shaking, for about 40 minutes or until no cloudiness is present. Transfer the solution to a 50-mL beaker. Wash the flask with two 5-mL portions of water and two 10-mL portions of alcohol, adding each washing to the beaker, and add 0.2 mL of nitric acid.
Reagent blank preparation—
Using a paper specimen wrapper, complete the combustion, and allow the mixture to stand for about 40 minutes or until no cloudiness is present, as directed under Test preparation. Transfer the solution so obtained to a 50-mL beaker. Wash the combustion flask with two 5-mL portions of water and two 10-mL portions of alcohol, adding the washings to the beaker, and add 0.2 mL of nitric acid.
Procedure—
Titrate the
Test preparation and the
Reagent blank preparation with 0.05 N silver nitrate VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically, using a silver-silver chloride electrode and a glass reference electrode (see
Titrimetry  541
541
). Determine the volume of 0.05 N silver nitrate VS consumed by the test specimen taken by the formula:
V 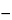 VB
VB,
in which
V and
VB are the volumes, in mL, of titrant used for the
Test preparation and the
Reagent blank preparation, respectively. Each mL of 0.05 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 1.773 mg of Cl: the chloride content is between 6.5% and 9.0%, calculated on the dried basis.
Water absorption—
Transfer about 5 g of Colestipol Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a dry, 100-mL plastic container, and add about 80 g of water, accurately weighed. Cover the container, and allow the suspension to equilibrate for 72 hours. With the aid of vacuum, filter the slurry transferred to a medium-porosity, fritted-glass funnel, and collect the filtrate in a tared plastic container. Disconnect the vacuum 2 minutes after the collection of the last portion of the filtrate. Weigh the container and the filtrate, and determine the weight, in g, of the filtrate. Determine the amount of water absorbed by subtracting the weight of the filtrate from the weight of water taken for the test, and divide the weight, in g, of the absorbed water by the weight, in g, of Colestipol Hydrochloride taken: each g absorbs between 3.3 g and 5.3 g of water.
Cholate binding capacity—
Cholate solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of sodium cholate and sodium chloride in water, and quantitatively dilute with water to obtain a solution having known concentrations of 10.0 mg of sodium cholate per mL and 9.0 mg of sodium chloride per mL. Adjust the solution by the dropwise addition of hydrochloric acid to a pH of 6.4 ± 0.1.
Test preparation—
Transfer 1.0 ± 0.01 g of Colestipol Hydrochloride to a glass-stoppered, 125-mL conical flask. Add 100.0 mL of Cholate solution, insert the stopper securely in the flask, shake vigorously for 90 minutes with the flask positioned horizontally on a platform shaker, remove the flask from the shaker, and allow the solids to settle for 5 minutes.
Procedure—
Transfer 20.0 mL of supernatant from the
Test preparation to a 40-mL beaker, transfer 20.0 mL of
Cholate solution to a second 40-mL beaker, and adjust both solutions by the dropwise addition of 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 10.5 ± 0.5. Titrate both solutions with 0.1 N hydrochloric acid VS, determining the endpoints potentiometrically, and measure the titrant volume corresponding to the difference between the midpoints of the two inflections in the titration curves obtained for each solution (see
Titrimetry  541
541
). Determine the volume of titrant equivalent to the bound cholate by subtracting the volume of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid VS used in titrating the
Test preparation from that used in titrating the
Cholate solution. Calculate the
Cholate binding capacity, in mEq per g, taken by the formula:
5VN / W,
in which
V is the volume, in mL, of titrant equivalent to the bound cholate;
N is the normality of the 0.1 N hydrochloric acid VS; and
W is the weight, in g, of Colestipol Hydrochloride taken for the
Test preparation. The
Cholate binding capacity is between 1.1 mEq per g and 1.6 mEq per g.
Water-soluble substances—
Transfer 5.0 g of Colestipol Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a glass-stoppered, 125-mL conical flask, add 80.0 mL of water, insert the stopper in the flask, and mount the flask in a water-bath shaker maintained at 37 ± 1
. Operate the shaker for 72 hours, remove the flask from the shaker, and filter the contents through a fine-porosity, fritted-glass funnel, collecting the filtrate in a tared 125-mL conical flask. Rinse any residual test material in the flask with two 5-mL portions of water, pass the washings through the filter, and combine the filtrates from the washings with the filtrate from the test mixture. Evaporate the filtrate to dryness, filtered air or nitrogen being used, if necessary, to aid in the evaporation. Dry the residue in a vacuum oven maintained at 75
for 1 hour, allow to cool in a desiccator, and weigh: not more than 0.5% of water-soluble substances is found in the portion of Colestipol Hydrochloride taken.
Organic volatile impurities, Method IV  467
467 :
:
meets the requirements.
Colestipol exchange capacity—
Resin base preparation—
Combine not less than 2 g of Colestipol Hydrochloride and 100 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide in a 125-mL conical flask, insert a stopper in the flask, secure the flask on a platform shaker, and shake the mixture for 3 to 4 hours. Filter the suspension through a coarse-porosity, fritted-glass funnel, and wash the resin with 500 mL of water. Transfer the resin to a 1000-mL beaker, add 200 mL of water, allow to stand for 10 minutes, filter the suspension, and check the pH of the filtrate. Repeat the washing procedure with 200-mL portions of water until the pH of the filtrate is below 8 (as much as 5000 mL of water may be required). Dry the colestipol base resin so obtained and the funnel at a pressure of about 5 mm of mercury at 60
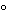
for 16 hours. Break up any aggregates, and store the
Resin base preparation in a desiccator.
Procedure—
Transfer about 1.0 g of the
Resin base preparation to a 125-mL conical flask, add 100.0 mL of 0.20 N hydrochloric acid, insert a stopper in the flask, and shake the mixture by mechanical means for 2.5 hours. Filter a portion of the suspension through a pledget of glass wool, and transfer 8.0 mL of the filtrate (test preparation) to a 25-mL beaker. Transfer 5.0 mL of the same 0.20 N hydrochloric acid that was used to equilibrate the resin to a second 25-mL beaker, and add 5.0 mL of water. Titrate both solutions with 0.2 N sodium hydroxide VS, determining the endpoints potentiometrically (see
Titrimetry  541
541
), and calculate the
Colestipol exchange capacity, in mEq per g, taken by the formula:
(100
N /
W)[(
Vb / 5)
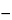
(
Va / 8)],
in which
N is the normality of the sodium hydroxide VS;
W is the weight, in g, of the
Resin base preparation taken;
Vb is the volume, in mL, of titrant used to neutralize the 5.0-mL aliquot of 0.20 N hydrochloric acid; and
Va is the volume, in mL, of titrant used to neutralize the residual acid in the test preparation. Each g exchanges not less than 9.0 mEq and not more than 11.0 mEq of sodium hydroxide, calculated as colestipol exchange capacity.

