Identification—
Prepare a solution of it containing about 12,000 Penicillin G Units per mL in a solvent mixture consisting of acetone, 0.1 M citric acid, and 0.1 M sodium citrate (2:1:1). Prepare a Standard solution of
USP Penicillin G Potassium RS containing about 12,000 Penicillin G Units per mL in the same solvent mixture. Apply separately 20 µL of each solution to a thin-layer chromatographic plate (see
Chromatography  621
621
) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture. Place the plate in a suitable chromatographic chamber, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of toluene, dioxane, and glacial acetic acid (90:25:4) until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow to air-dry. Spray the plate with
starch TS followed by dilute iodine TS (1 in 10). Penicillin G appears as a white spot on a purple background: the
RF value of the penicillin G spot obtained from the test solution corresponds to that obtained from the Standard solution.
pH  791
791 :
:
between 5.0 and 7.5, in a solution containing 60 mg per mL, or, where packaged for dispensing, in the solution constituted as directed in the labeling, except where it is labeled as containing sodium citrate it is between 6.0 and 8.5.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
—
Dry about 100 mg, accurately weighed, in a capillary-stoppered bottle in vacuum at 60
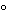
for 3 hours: it loses not more than 1.5% of its weight.
Assay—
Mobile phase, Standard preparation, Resolution solution, and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay under
Penicillin G Potassium.
Assay preparation 1
(where it is represented as being in a single-dose container)—Constitute Penicillin G Potassium for Injection as directed in the labeling. Withdraw all of the withdrawable contents, using a hypodermic needle and syringe, and quantitatively dilute with water to obtain a solution containing about 160 Penicillin G Units per mL.
Assay preparation 2
(where the label states the quantity of penicillin G in a given volume of constituted solution)—Constitute Penicillin G Potassium for Injection as directed in the labeling. Quantitatively dilute an accurately measured volume of the constituted solution with water to obtain a solution containing about 160 Penicillin G Units per mL.
Assay preparation 3
(where it contains Sodium Citrate)—Transfer about 50 mg of the Penicillin G Potassium for Injection, accurately weighed, to a 500-mL volumetric flask, add about 400 mL of water, and shake to dissolve. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for
Procedure in the
Assay under
Penicillin G Potassium. Calculate the number of Penicillin G Units in the container or in the portion of constituted solution taken by the formula:
(L/D)(PWS / 50)(rU / rS),
in which
L is the labeled quantity of Penicillin G Units in the container or in the volume of constituted solution taken;
D is the concentration, in Penicillin G Units per mL, of
Assay preparation 1 or
Assay preparation 2, on the basis of the labeled quantity in the container or in the portion of constituted solution taken and the extent of dilution;
P is the specified potency, in Penicillin G Units per mg, of
USP Penicillin G Potassium RS;
WS is the weight, in mg, of
USP Penicillin G Potassium RS taken to prepare the
Standard preparation; and
rU and
rS are the penicillin G peak responses obtained from the
Assay preparation and the
Standard preparation, respectively. Calculate the potency, in Penicillin G Units per mg, of the Penicillin G Potassium for Injection taken by the formula:
10(WS / WU)(P)(rU / rS),
in which
WS and
WU are the weights, in mg, of
USP Penicillin G Potassium RS and Penicillin G Potassium for Injection taken to prepare the
Standard preparation and
Assay preparation 3, respectively, and the other terms are as defined above. Perform the above procedure on 10 containers (where it is represented as being in a single-dose container) and, if necessary, on 10 containers (where the label states the quantity of penicillin G in a given volume of constituted solution). Use the individual results to determine the
Uniformity of dosage units and the average thereof as the
Assay value.

