A:
SDS-PAGE—
Molecular weight marker—
Use a suitable molecular weight marker (MWM) containing protein bands between 20 and 200 kD.
PBS solution—
Prepare a solution that contains 8065.0 mg and 200.0 mg of sodium chloride and potassium chloride, respectively, per L of 0.01 M sodium phosphate buffer, pH 7.4.
4X Sample buffer2 —
Dissolve 0.666 g of tris-hydrochloride, 0.682 g of tris base, 0.800 g of lithium dodecyl sulfate (LDS), 0.006 g of ethylenedinitrilotetraacetic acid (EDTA), and 4 g of glycerol in 8 mL of water; add 0.75 mL of 1% Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 (see Coomassie Blue G-250 in
Reagents under
Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions) solution and 0.25 mL of 1% phenol red solution. Mix well, and adjust the volume with water to 10 mL.
2X Sample buffer—
Prepare a mixture of 4X Sample buffer and water (1:1).
1X Sample buffer—
Prepare a mixture of 2X Sample buffer and water (1:1).
1 M Dithiothreitol solution—
Dissolve 0.154 g of dl-dithiothreitol (DTT) in 1 mL of water.
2X Reducing sample buffer—
Mix 180 µL of 2X Sample buffer and 20 µL of 1 M Dithiothreitol solution.
20X Running buffer3 —
Dissolve 104.6 g of 3-(
N-morpholino)propanesulfonic acid (MOPS), 60.6 g of tris base, 10 g of sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), and 3.0 g of EDTA in 400 mL of water. Mix well, and adjust with water to 500 mL.
1X Running buffer—
Prepare a solution of water and 20X Running buffer (19:1).
Gel staining solution—
Prepare a solution of Coomassie brilliant blue R-250 (see Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-250 in Reagents under Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions) having a concentration of 0.5 g per L in a mixture of water, isopropanol, and acetic acid (6.5:2.5:1.0). Filter, and store at room temperature. Silver staining is not recommended.
Destaining solution—
Mix 100 mL of acetic acid with 900 mL of water.
Standard preparation—
Dilute USP rProtein A RS to 0.4 mg per mL with
PBS solution. Further dilute this solution 1:1 with
2X Reducing sample buffer, and incubate in a closed tube for 5 minutes at 90
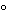
. Mix, and quick spin prior to loading.
Test preparation—
Dilute rProtein A with PBS solution to 0.4 mg per mL. Proceed as directed under Standard preparation beginning with “Further dilute.”
Comix solution—
Dilute rProtein A and USP rProtein A RS with PBS solution to 0.8 mg per mL. This solution contains 0.4 mg per mL of each protein. Proceed as directed under Standard preparation beginning with “Further dilute.”
SDS-PAGE gel and apparatus set-up—
Assemble gel apparatus following the manufacturer’s instructions. Lock the gel tension wedge in place, and fill approximately 200 mL of
1X Running buffer into the inside chamber. If there are no leaks, pour 600 mL of
1X Running buffer into the outer chamber. Gently pull the comb out of the cassette to immerse the wells in
1X Running buffer. Load 10 µL of each preparation as directed below under
Gel loading onto a 10% Bis-Tris SDS-PAGE gel.
4
Gel loading—
Use the following gel loading scheme when running one
Test preparation (see
Table 1). Each
Test preparation is run by itself and as part of the
Comix solution that contains the rProtein A and USP rProtein A RS.
Table 1
| Lane |
Sample |
Load
Volume
(µL) |
Load
Amount
(µg) |
| 1 |
1X Sample buffer |
10 |
N/A |
| 2 |
MWM |
20 |
N/A |
| 3 |
Test preparation #1 |
10 |
2 |
| 4 |
Comix solution #1 |
10 |
4 (total) |
| 5 |
Test preparation #1 |
10 |
2 |
| 6 |
1X Sample buffer |
10 |
N/A |
| 7 |
Standard preparation |
10 |
2 |
| 8 |
MWM |
20 |
N/A |
| 9 |
— |
— |
— |
| 10 |
— |
— |
— |
Running the gel—
Set the voltage to 125 volts, and run at a constant voltage. Run the gels until the bromophenol blue band is approximately 5 mm from the bottom of the gel (approximately 120 to 140 minutes).
Gel staining—
Pour approximately 100 mL of Gel staining solution into the staining container. Place the gel into the staining container, and allow the stain to completely cover the gel. Cook the gel and container in a microwave for 30 seconds. Place the staining container on an orbital shaker, and stain the gel for 1 hour with gentle shaking.
Destaining—
Drain the Gel staining solution, and add enough Destaining solution to the container to cover the gel. Place the container on an orbital shaker, and shake at low speed. Change the Destaining solution as necessary until a clear background is obtained. After destaining, rinse the gel thoroughly with water, and leave the gel in water for 10 minutes before scanning.
Gel scanning—
Apply some water to the glass plate of the scanner, and place the gels on a wetted glass plate. Eliminate any bubbles. Using appropriate settings, scan the gels.
Data analysis—
Choose a band between the 20 kD and 30 kD bands of the MWM to calculate the percentage of the retention factor. Draw a line in one lane (lane containing
1X Sample buffer) from the well to the apex (region of greatest intensity) of the chosen band.
The length of this line is denoted as the total distance (DT). For the lanes containing samples draw a line from the well to the apex of each band. For each band the length of this distance is the migration distance (DM) in mm. Record the DT and DM on the report sheet for each peak or band. The total distance should be the same for each lane on a gel. Calculate the percentage of the retention factor (RF) of each major peak or band, and document on the report sheet using the following equation:
%RF = DM / DT × 100
Also for each gel, record the number of bands and approximate molecular weight of each band in each sample.
System suitability—
All bands between 20 kD and 70 kD are present. The lane containing 1X Sample buffer does not contain any bands.
Specificity—
The rProtein A has one major band and a similar molecular weight that corresponds to those of the USP rProtein A RS. The Comix solution also shows a single major band.
B:
IgG Binding—
[Note—The IgG binding assay is a functional method for determining the percentage of rProtein A capable of binding to immobilized human polyclonal immunoglobulin. Since the percent of functional rProtein A in each lot is not less than 95%, the assay measures unbound protein versus total protein injected. This is done by comparing the absorbance in the flow-through to absorbance from an injection bypassing the column.
]
Sample pretreatment (desalting)—
In order to remove any buffer components that may contribute to absorbance in the “unbound” IgG column fraction, samples are desalted with
Solution A. Desalting may be performed using a suitable desalting column
5 depending on the volumes required.
IgG column—
A 1-mL Sepharose column
6 with immobilized human polyclonal IgG (hIgG) is required to perform this assay.
[Note—The IgG column requires washing when it is new, when it has performed several analysis cycles, or after system suitability failure. Column washing procedure is not required for each sample injection.
]
Column washing solution A—
Prepare a solution of 0.5 M acetic acid, pH 3.4 by adding 28.6 mL of acetic acid into a 1000-mL beaker, diluting to 900 mL with water, and adjusting with ammonium acetate to a pH of 3.4. Transfer the solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Pass the solution through a 0.45-µm membrane filter.
Column washing solution B—
Prepare a solution of 50 mM Tris, pH 7.6, 150 mM sodium chloride, and 0.05% Tween 20 by the following procedure. Add 6.06 ± 0.01 g of Tris and 8.77 ± 0.01 g of sodium chloride into a 1000-mL beaker. Dilute with water to 900 mL, and adjust with 0.5 M sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.60 ± 0.05. Transfer the solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Pass the solution through a 0.45-µm membrane filter (buffer solution). Add 0.5 mL of Tween 20 into 1 L of the buffer solution and mix thoroughly.
Solution A—
Prepare a solution of 20 mM monobasic sodium phosphate and 150 mM sodium chloride, pH 7.6 by the following procedure. Add 2.76 ± 0.01 g monobasic sodium phosphate hydrate and 8.77 ± 0.01 g sodium chloride into a 1000-mL beaker. Dilute with water to 900 mL, and adjust with 5 M sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.60 ± 0.05. Transfer the solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Pass the solution through a 0.45-µm membrane filter.
Solution B—
Prepare a solution of 100 mM phosphoric acid pH 2.8 by the following procedure. Add 6.8 mL of phosphoric acid into a 1000-mL beaker. Dilute with water to 900 mL, and adjust with 2 M potassium hydroxide to a pH of 2.80 ± 0.05. Transfer the solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of
Solution A and
Solution B as directed for
Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see
System Suitability under
Chromatography  621
621
).
Standard preparation—
Thaw USP rProtein A RS, and use directly.
Test preparation—
Prepare a 4.0 to 6.0 mg per mL rProtein A solution in Solution A.
Chromatographic system—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 1-mL column with immobilized hIgG. The chromatograph is equipped with a bypass valve to allow flow to be diverted from the column. Each analysis consists of a series of two injections, one where the sample is injected onto the column and one where the sample bypasses the column and flows directly into the detector. Perform three replicate analyses. The chromatograph is programmed as follows (see
Table 2).
Table 2
Flow Rate
(mL per minute) |
Time
(minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Valve
Position |
 Elution Elution |
| 1.0 |
0–6 |
100 |
0 |
column |
re-equilibration |
| 1.0 |
6–12 |
100®0 |
0®100 |
column |
re-equilibration |
| 1.0 |
12–22 |
100 |
0 |
column |
equilibration |
| 0.4 |
22–25 |
100 |
0 |
column |
equilibration |
0.4 (sample
injected) |
25–35 |
100 |
0 |
column |
isocratic |
| 1.0 |
35–49 |
100®0 |
0®100 |
column |
regeneration |
| 1.0 |
49–63 |
0®100 |
100®0 |
column |
re-equilibration |
| 1 |
63–65 |
100 |
0 |
bypass |
equilibration |
| 0.4 |
65–68 |
100 |
0 |
bypass |
equilibration |
0.4 (sample
injected) |
68–75 |
100 |
0 |
bypass |
isocratic |
Chromatograph the
Standard preparation, record the peak responses, and calculate the percentage of hIgG binding as directed for
Procedure: the percentage of hIgG binding
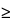
95% and the relative standard deviation for replicate analysis is not more than 1%.
Procedure—
Inject a volume (about 100 µL) of the
Test preparation. Record the chromatogram, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of hIgG binding activity by the following formula:
100 – 100(rC / rB)
in which
rC is the unbound material peak response from the column injection and
rB is the bypass peak response from the bypass injection. Each replicate analysis of the
Test preparation is not less than 95% of hIgG binding. Report the average value from three replicate analyses.

