This general chapter is harmonized with the corresponding texts of the European Pharmacopoeia and/or the Japanese Pharmacopoeia. The texts of these pharmacopeias are therefore interchangeable, and the methods of the European Pharmacopoeia and/or the Japanese Pharmacopoeia may be used for demonstration of compliance instead of the present general chapter. These pharmacopeias have undertaken not to make any unilateral change to this harmonized chapter.
Portions of the present general chapter text that are national
USP text, and therefore not part of the harmonized text, are marked with symbols (
) to specify this fact.
This test is provided to determine whether tablets or capsules disintegrate within the prescribed time when placed in a liquid medium at the experimental conditions presented below.
Compliance with the limits on
Disintegration stated in the individual monographs is required except where the label states that the tablets or capsules are intended for use as troches, or are to be chewed, or are designed as extended-release dosage forms or delayed-release dosage forms. Determine the type of units under test from the labeling and from observation, and apply the appropriate procedure to 6 or more dosage units.
For the purposes of this test, disintegration does not imply complete solution of the unit or even of its active constituent. Complete disintegration is defined as that state in which any residue of the unit, except fragments of insoluble coating or capsule shell, remaining on the screen of the test apparatus or adhering to the lower surface of the disk, if used, is a soft mass having no palpably firm core.
APPARATUS
The apparatus consists of a basket-rack assembly, a 1000-mL, low-form beaker, 138 to 160 mm in height and having an inside diameter of 97 to 115 mm for the immersion fluid, a thermostatic arrangement for heating the fluid between 35
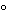
and 39
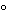
, and a device for raising and lowering the basket in the immersion fluid at a constant frequency rate between 29 and 32 cycles per minute through a distance of not less than 53 mm and not more than 57 mm. The volume of the fluid in the vessel is such that at the highest point of the upward stroke the wire mesh remains at least 15 mm below the surface of the fluid and descends to not less than 25 mm from the bottom of the vessel on the downward stroke. At no time should the top of the basket-rack assembly become submerged. The time required for the upward stroke is equal to the time required for the downward stroke, and the change in stroke direction is a smooth transition, rather than an abrupt reversal of motion. The basket-rack assembly moves vertically along its axis. There is no appreciable horizontal motion or movement of the axis from the vertical.
Basket-Rack Assembly—
The basket-rack assembly consists of six open-ended transparent tubes, each 77.5 ± 2.5 mm long and having an inside diameter of 20.7 to 23 mm and a wall 1.0 to 2.8 mm thick; the tubes are held in a vertical position by two plates, each 88 to 92 mm in diameter and 5 to 8.5 mm in thickness, with six holes, each 22 to 26 mm in diameter, equidistant from the center of the plate and equally spaced from one another. Attached to the under surface of the lower plate is a woven stainless steel wire cloth, which has a plain square weave with 1.8- to 2.2-mm apertures and with a wire diameter of 0.57 to 0.66 mm. The parts of the apparatus are assembled and rigidly held by means of three bolts passing through the two plates. A suitable means is provided to suspend the basket-rack assembly from the raising and lowering device using a point on its axis.
The design of the basket-rack assembly may be varied somewhat, provided the specifications for the glass tubes and the screen mesh size are maintained. The basket-rack assembly conforms to the dimensions found in
Figure 1.
Disks—
The use of disks is permitted only where specified or allowed
in the monograph. If specified in the individual monograph,
each tube is provided with a cylindrical disk 9.5 ± 0.15 mm thick and 20.7 ± 0.15 mm in diameter. The disk is made of a suitable transparent plastic material having a specific gravity of between 1.18 and 1.20. Five parallel 2 ± 0.1-mm holes extend between the ends of the cylinder. One of the holes is centered on the cylindrical axis. The other holes are centered 6 ± 0.2 mm from the axis on imaginary lines perpendicular to the axis and parallel to each other. Four identical trapezoidal-shaped planes are cut into the wall of the cylinder, nearly perpendicular to the ends of the cylinder. The trapezoidal shape is symmetrical; its parallel sides coincide with the ends of the cylinder and are parallel to an imaginary line connecting the centers of two adjacent holes 6 mm from the cylindrical axis. The parallel side of the trapezoid on the bottom of the cylinder has a length of 1.6 ± 0.1 mm, and its bottom edges lie at a depth of 1.6 ± 0.1 mm from the cylinder's circumference. The parallel side of the trapezoid on the top of the cylinder has a length of 9.4 ± 0.2 mm, and its center lies at a depth of 2.6 ± 0.1 mm from the cylinder's circumference. All surfaces of the disk are smooth. If the use of disks is specified
in the individual monograph
, add a disk to each tube, and operate the apparatus as directed under
Procedure. The disks conform to dimensions found in
Figure 11.
Fig. 1. Disintegration apparatus. (All dimensions are expressed in mm.)
PROCEDURE
 Uncoated Tablets—
Uncoated Tablets—
Place 1 dosage unit in each of the six tubes of the basket and, if prescribed, add a disk. Operate the apparatus, using
water or
the specified medium as the immersion fluid, maintained at 37 ± 2
. At the end of the time limit specified
in the monograph,
lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets have disintegrated completely. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets. The requirement is met if not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested are disintegrated.
 Plain-Coated Tablets—
Plain-Coated Tablets—
Apply the test for
Uncoated Tablets, operating the apparatus for the time specified in the individual monograph.
Delayed-Release (Enteric-Coated) Tablets—
Place 1 tablet in each of the six tubes of the basket and, if the tablet has a soluble external sugar coating, immerse the basket in water at room temperature for 5 minutes. Then operate the apparatus using
simulated gastric fluid TS maintained at 37 ± 2
as the immersion fluid. After 1 hour of operation in
simulated gastric fluid TS, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: the tablets show no evidence of disintegration, cracking, or softening. Operate the apparatus, using
simulated intestinal fluid TS maintained at 37 ± 2
as the immersion fluid, for the time specified in the monograph. Lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets disintegrate completely. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
Buccal Tablets—
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. After 4 hours, lift the basket from the fluid, and observe the tablets: all of the tablets have disintegrated. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
Sublingual Tablets—
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. At the end of the time limit specified in the individual monograph: all of the tablets have disintegrated. If 1 or 2 tablets fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional tablets: not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 tablets tested disintegrate completely.
Hard Gelatin Capsules—
Apply the test for Uncoated Tablets. Attach a removable wire cloth, which has a plain square weave with 1.8- to 2.2-mm mesh apertures and with a wire diameter of 0.60 to 0.655 mm, as described under Basket-Rack Assembly, to the surface of the upper plate of the basket-rack assembly. Observe the capsules within the time limit specified in the individual monograph: all of the capsules have disintegrated except for fragments from the capsule shell. If 1 or 2 capsules fail to disintegrate completely, repeat the test on 12 additional capsules: not fewer than 16 of the total of 18 capsules tested disintegrate completely.
Soft Gelatin Capsules—
Proceed as directed under
Hard Gelatin Capsules.