Chromatographic purity—
Phosphate buffer pH 7.6—
Dissolve 0.725 g of monobasic sodium phosphate and 4.472 g of anhydrous dibasic sodium phosphate in 300 mL of water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Dilute 250 mL of this solution with water to 1000 mL. If necessary, adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.6.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of
Phosphate buffer pH 7.6 and acetonitrile (72.5:27.5). Make adjustments if necessary (see
System Suitability under
Chromatography  621
621
).
[Note—To improve the resolution, the composition may be changed to 75:25, if necessary.
]
Test solution—
Dissolve about 4 mg of Esomeprazole Magnesium in 25 mL of Mobile phase. [Note—Prepare this solution fresh.]
System suitability solution—
Dissolve about 1 mg of
USP Omeprazole RS and 1 mg of USP Omeprazole Related Compound A RS in about 25 mL of
Mobile phase.
[Note—Omeprazole Related Compound A is omeprazole sulfone.
]
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.0-mm × 12.5-cm or a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L7. (Alternatively, a 3.9-mm × 15-cm column that contains 4-µm packing L1 may be used.) The flow rate is about 0.8 to 1.0 mL per minute. Chromatograph the
System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the relative retention times for omeprazole related compound A and omeprazole are about 0.8 and 1.0, respectively; the resolution,
R, between omeprazole related compound A and omeprazole is not less than 3.
Procedure—
Inject a volume of about 50 µL of the
Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram for at least 4.5 times the retention time of the omeprazole peak, and measure the peak responses. Identify the impurities based on the retention times shown in
Table 1.
Table 1
| Name |
Relative Retention Time |
Limit
(%) |
| Omeprazole N-oxide1 |
0.45 |
0.1 |
| Omeprazole Sulfone2 (Related Compound A) |
0.8 |
0.2 |
| Omeprazole |
1.0 |
n/a |
|
1
4-methoxy-2-[[(RS)-(5-methoxy-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)sulfinyl]methyl]-3,5-dimethylpyridine 1-oxide.
2
5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethylpyridin-2-yl)methyl]sulfonyl]-1H-benzimidazole.
|
Calculate the percentage of any individual impurity in the portion of Esomeprazole Magnesium taken by the formula:
100(ri / rs)
in which
ri is the peak response of any individual impurity, and
rs is the sum of the responses of all the peaks: in addition to not exceeding the limits in
Table 1, not more than 0.1% of any other individual impurity is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found.
Enantiomeric purity—
Phosphate buffer pH 6—
Mix 70 mL of 1 M monobasic sodium phosphate with 20 mL of 0.5 M dibasic sodium phosphate, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. Dilute 250 mL of this solution with water to 1000 mL.
Diluent pH 11—
Mix 11 mL of 0.25 M tribasic sodium phosphate with 22 mL of 0.5 M dibasic sodium phosphate, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of Phosphate buffer pH 6 and acetonitrile (425:75).
System suitability solution—
Dissolve about 2 mg of
USP Omeprazole RS in 10 mL of
Diluent pH 11. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution with
Diluent pH 11 to 50 mL.
Test solution—
Dissolve about 40 mg of Esomeprazole Magnesium in 5 mL of methanol, and dilute with Diluent pH 11 to 25 mL. Dilute 1 mL of this solution with Diluent pH 11 to 50 mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 302-nm detector and a 4.0-mm × 10-cm column that contains packing L41. The flow rate is about 0.6 mL per minute. Chromatograph the
System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure. The elution order is the
R-enantiomer, followed by the esomeprazole peak, which is the
S-enantiomer. The resolution,
R, between the enantiomer peaks is not less than 3.
Procedure—
Inject a volume of about 20 µL of the
Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of the
R-enantiomer in the esomeprazole by the formula:
100(rU / rs)
in which
rU is the peak response for the
R-enantiomer, and
rs is the sum of the responses of both the esomeprazole and
R-enantiomer peaks. Not more than 0.2% of the
R-enantiomer is found.
Content of magnesium—
Lanthanum solution—
Transfer 58.7 g of lanthanum oxide into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, wet the substance with some water, and dissolve by cautious addition of 250 mL of hydrochloric acid in 20- to 30-mL portions, cooling between the additions. Add water while stirring, cool to room temperature, and dilute with water to volume. [Note—Store the solution in a plastic bottle.]
Magnesium standard stock solution—
Quantitatively dilute a suitable amount of a commercially prepared atomic absorption standard solution for magnesium with water to obtain a solution containing 1000 µg of magnesium per mL. [Note—Store the solution in a plastic bottle.]
Magnesium intermediate standard solution—
Transfer 10.0 mL of Magnesium standard stock solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, add 50 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 20.0 mL of this solution to a 200-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 2 µg of magnesium per mL.
Standard solutions—
Transfer 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, and 25.0 mL of Magnesium intermediate standard solution to separate 100-mL volumetric flasks. To each flask, add 4.0 mL of Lanthanum solution, and dilute with water to volume. These Standard solutions contain 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, and 0.5 µg of magnesium per mL, respectively. [Note—Concentrations of the Standard solutions and the Test solution may be modified to fit the linear or working range of the instrument. When using instruments with a linear calibration graph, the number of Standard solutions can be reduced.]
Blank solution—
Transfer 4.0 mL of Lanthanum solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Test solution—
Transfer about 250 mg of Esomeprazole Magnesium, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 20 mL of 1 N hydrochloric acid, swirl until dissolved, and dilute with water to volume. Allow to stand for 30 minutes. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution to a 200-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 10.0 mL of the solution so obtained to another 100-mL volumetric flask, add 4.0 mL of Lanthanum solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the
Standard solution, the
Blank solutions, and the
Test solution at the magnesium emission line at 285.2 nm with a suitable atomic absorption spectrophotometer (see
Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering  851
851
) using an air–acetylene flame. Determine the concentration,
C, in µg per mL, of magnesium in the
Test solution using the calibration graph. Calculate the content of magnesium, in percent, in the portion of Esomeprazole Magnesium taken by the formula:
100(0.001
CD /
W)[100 / (100
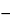 L
L)]
in which
C is as defined above; the multiplier 0.001 is for conversion of µg per mL to mg per mL;
D is the dilution factor for the
Test solution; W is the amount of Esomeprazole Magnesium, in mg, taken to prepare the
Test solution; and
L is the content of water, in percent, as determined in the test for
Water. The magnesium content, calculated on the anhydrous basis, is between 3.30% and 3.55%.
Assay—
Phosphate buffer pH 7.6—
Dissolve 0.725 g of monobasic sodium phosphate and 4.472 g of anhydrous dibasic sodium phosphate in 300 mL of water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Dilute 250 mL of this solution with water to 1000 mL. If necessary, adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.6.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of Phosphate buffer pH 7.6 and acetonitrile (650:350).
Phosphate buffer pH 11—
Mix 11 mL of 0.25 M tribasic sodium phosphate with 22 mL of 0.5 M dibasic sodium phosphate, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Standard preparation—
Transfer about 10 mg of
USP Omeprazole RS, accurately weighed, to a 200-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in about 10 mL of methanol. Add 10 mL of
Phosphate buffer pH 11, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains about 0.05 mg of omeprazole per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 10 mg of Esomeprazole Magnesium, accurately weighed, to a 200-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in about 10 mL of methanol, add 10 mL of Phosphate buffer pH 11, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains about 0.05 mg of esomeprazole magnesium per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.0-mm × 12.5-cm or a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L7. (Alternatively, a 3.9-mm × 15-cm column that contains 4-µm packing L1 may be used.) The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the
Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for
Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 2000 theoretical plates; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the
Standard preparation and the
Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of C
34H
36MgN
6O
6S
2 in the portion of Esomeprazole Magnesium taken by the formula:
100[713.12 / (2 × 345.42)](CS / CU)(rU / rS)
in which 713.12 and 345.42 are the molecular weights of esomeprazole magnesium and omeprazole, respectively;
CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of omeprazole in the
Standard preparation; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of esomeprazole magnesium in the
Assay preparation; and
rU and
rS are the peak responses obtained from the
Assay preparation and the
Standard preparation, respectively.
 1S (USP31)
1S (USP31)


 .
.