Protein—
Transfer about 10 g of Maltodextrin, accurately weighed, to an 800-mL Kjeldahl flask, and add 10 g of anhydrous potassium sulfate or sodium sulfate, 300 mg of copper selenite or mercuric oxide, and 60 mL of sulfuric acid. Gently heat the mixture, keeping the flask inclined at about a 45
angle, and after frothing has ceased, boil briskly until the solution has remained clear for about 1 hour. Cool, very cautiously add about 50 mL of water while swirling to dissipate the resulting heat. Add an additional 150 to 250 mL of water, mix, and cool again. Cautiously pour about 75 mL (or enough to make the mixture strongly alkaline) of sodium hydroxide solution (2 in 5) down the inside of the flask so that it forms a layer under the acid solution, and then add a few pieces of granular zinc. Immediately connect the flask to a distillation apparatus consisting of a Kjeldahl connecting bulb and a condenser, the delivery tube of which extends well beneath the surface of an accurately measured excess of 0.1 N sulfuric acid contained in a 500-mL flask. Gently rotate the contents of the Kjeldahl flask to mix, and distill until all ammonia has passed into the absorbing acid solution (about 250 mL of distillate). To the receiving flask add 0.25 mL of methyl red-methylene blue TS, and titrate the excess acid with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide. Perform a blank determination, substituting pure sucrose or dextrose for the test specimen, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N sulfuric acid consumed is equivalent to 1.401 mg of nitrogen (N). Calculate the percentage of N in the specimen taken, and then calculate the percentage of protein by multiplying the percentage of N by 6.25. The limit is 0.1%.
Sulfur dioxide—
Hydrogen peroxide solution—
Dilute 30 percent hydrogen peroxide with water to obtain a 3% solution. Just before use, add 3 drops of
methyl red TS, and neutralize to a yellow endpoint with 0.01 N sodium hydroxide. Do not exceed the endpoint.
Nitrogen—
Use high-purity nitrogen, with a flow regulator that will maintain a flow of 200 ± 10 mL per minute. Guard against the presence of oxygen by passing the nitrogen through a scrubber, such as alkaline pyrogallol, prepared as follows. Add 4.5 g of pyrogallol to a gas-washing bottle, purge the bottle with nitrogen for 3 minutes, and add a solution containing 85 mL of water and 65 g of potassium hydroxide, while maintaining an atmosphere of nitrogen in the bottle.
Apparatus—
The apparatus (see
Fig. 1) is designed to effect the selective transfer of sulfur dioxide from the specimen in boiling aqueous hydrochloric acid to the
Hydrogen peroxide solution. The backpressure is limited to the unavoidable pressure due to the height of the
Hydrogen peroxide solution above the tip of the bubbler,
F. Keeping the backpressure as low as possible reduces the likelihood that sulfur dioxide will be lost through leaks. Preboil vinyl and silicone tubing. Apply a thin film of stopcock grease to the sealing surfaces of all of the joints except the joint between the separatory funnel and the flask, and clamp the joints to ensure tightness. The separatory funnel,
B, has a capacity of 100 mL or greater. The inlet adapter,
A, with a hose connector provides a means of applying headpressure over the solution.
[NOTE—A pressure-equalizing dropping funnel is not recommended because condensate, which may contain sulfur dioxide, is deposited in the funnel and the side arm.
]
Fig. 1. Apparatus for Sulfur dioxide test.
The round-bottom flask,
C, is a 1000-mL flask with three 24/40 tapered joints. The gas inlet tube,
D, is long enough to permit introduction of the nitrogen within 2.5 cm of the bottom of the flask. The Allihn condenser,
E, has a jacket length of 300 mm. The bubbler,
F, (see
Fig. 2) is fabricated from glass according to the dimensions given in Figure 2. The
Hydrogen peroxide solution is contained in a vessel,
G, having an inside diameter of about 2.5 cm and a depth of about 18 cm. Circulate coolant, such as a mixture of water and methanol (4:1) maintained at 5
, to chill the condenser.
Fig. 2. Bubbler (F) for Sulfur Dioxide Apparatus.
Procedure—
Position the
Apparatus in a heating mantle controlled by a power-regulating device. Add 400 mL of water to the flask. Close the stopcock of the separatory funnel, and add 90 mL of 4 N hydrochloric acid to the separatory funnel. Begin the flow of nitrogen at a rate of 200 ± 10 mL per minute. Start the condenser coolant flow. Add 30 mL of
Hydrogen peroxide solution to vessel
G. After 15 minutes, remove the separatory funnel, and transfer a mixture of 50.0 g of Maltodextrin, accurately weighed, and 100 mL of alcohol solution (5 in 100). Apply stopcock grease to the outer joint of the separatory funnel, return the separatory funnel to the tapered joint flask, and concomitantly resume the nitrogen flow. Apply headpressure above the hydrochloric acid solution in the separatory funnel with a rubber bulb equipped with a valve. Open the stopcock of the separatory funnel to permit the hydrochloric acid solution to flow into the flask. Continue to maintain sufficient pressure above the hydrochloric acid solution to force it into the flask.
[NOTE—The stopcock may be temporarily closed, if necessary, to pump up the pressure.
] To guard against escape of sulfur dioxide into the separatory funnel, close the stopcock before the last few mL of hydrochloric acid drain out. Apply power to the heating mantle sufficient to cause about 85 drops of reflux per minute. After refluxing for 1.75 hours, remove vessel
G, add 3 drops of
methyl red TS, and titrate the contents with 0.01 N sodium hydroxide VS, using a 10-mL buret with an overflow tube and a hose connection to a carbon dioxide-absorbing tube, to a yellow endpoint that persists for at least 20 seconds. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction (see
Titrimetry  541
541
). Calculate the quantity, in µg, of SO
2 in each g of the Maltodextrin taken by the formula:
1000(32.03)VN / W,
in which 32.03 is the milliequivalent weight of sulfur dioxide;
V is the volume, in mL, of titrant consumed;
N is the normality of the titrant; and
W is the weight, in g, of Maltodextrin taken. Not more than 40 µg of sulfur dioxide per g of Maltodextrin are found (.004%).
Dextrose equivalent—
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of
USP Dextrose RS in water, and dilute quantitatively with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 10 mg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 5 g of Maltodextrin, accurately weighed, with the aid of hot water to a 100-mL volumetric flask, cool, add water to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Transfer 25.0-mL portions of
alkaline cupric tartrate TS to each of two boiling flasks. Bring the contents of one flask to boiling within about 2 minutes while titrating with
Standard solution to within 0.5 mL of the anticipated endpoint. Boil gently for 2 minutes. Continue to boil gently, add 2 drops of methylene blue solution (1 in 100), and complete the titration within 1 minute by adding the
Standard solution dropwise or in small increments until the blue color disappears, determined by viewing against a white background in daylight or under equivalent illumination. If more than 0.5 mL of the titrant was required after the addition of the indicator, repeat the titration, adding the necessary volume of titrant before adding the indicator. Bring the contents of the second flask to boiling, and similarly titrate with
Test solution. Calculate the
Dextrose equivalent, on the dried basis, taken by the formula:
[100 / (1
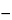
0.01
A)](
CS / CU)(
VS / VU),
in which
A is the percentage
Loss on drying of the Maltodextrin taken;
CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Maltodextrin in the
Test solution;
CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of
USP Dextrose RS in the
Standard solution; and
VU and
VS are the titrated volumes, in mL, of the
Test solution and the
Standard solution, respectively. The
Dextrose equivalent is less than 20.
[NOTE—This is a limit test. For Maltodextrins with lower reducing values, other procedures may give other results.
]

