This chapter provides guidance on the identification and performance of procedures for evaluating the biocompatibility of drug containers, elastomeric closures, medical devices, and implants. Biocompatibility refers to the tendency of these products to remain biologically inert throughout the duration of their contact with the body. The biocompatibility testing procedures referenced in this chapter are designed to detect the nonspecific, biologically reactive, physical or chemical characteristics of medical products or the materials used in their construction. In combination with chemical assays, these biological procedures can be used to detect and identify the inherent or acquired toxicity of medical products prior to or during their manufacturing and processing.
Preclinical testing procedures to evaluate the safety of the elastomers, plastics, or other polymers used in the construction of medical products are referenced or described in the following general chapters: Injections  1
1 , Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
, Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 , Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
, Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 , Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices
, Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices  161
161 , Elastomeric Closures for Injections
, Elastomeric Closures for Injections  381
381 , and Containers—Plastics
, and Containers—Plastics  661
661 . Specific in vitro and in vivo testing procedures to evaluate the biocompatibility of medical products in patients are described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
. Specific in vitro and in vivo testing procedures to evaluate the biocompatibility of medical products in patients are described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 and under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
and under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 .
.
The procedures used to evaluate the biocompatibility of a medical product or its construction materials have been categorized as a panel of biological effects (toxicity procedures): cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation or intracutaneous reactivity, acute systemic toxicity, subchronic toxicity (subacute toxicity), genotoxicity, implantation, hemocompatibility, chronic toxicity (extending beyond 10% of the life span of the test animal or beyond 90 days), carcinogenicity, reproductive or developmental toxicity, and biodegradation.1 The USP general chapters referring to the toxicity procedures for these categories are indicated in Table 1. In addition, pyrogenicity, an area of special toxicity, is evaluated under Pyrogen Test  151
151 and under Bacterial Endotoxins Test
and under Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 . There are currently no general chapters that detail sensitization, subchronic toxicity, genotoxicity, chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, hemotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, or biodegradation testing requirements.
. There are currently no general chapters that detail sensitization, subchronic toxicity, genotoxicity, chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, hemotoxicity, reproductive toxicity, or biodegradation testing requirements.
Table 1. Toxicity Procedures in the USP General Chapters
| Biological Effect | USP General Chapter |
| Cytotoxicity | Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro |
| Sensitization | [to come] |
| Irritation or intracutaneous reactivity | Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo |
| Systemic toxicity (acute toxicity) | Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo |
| Subchronic toxicity (subacute toxicity) | [to come] |
| Genotoxicity | [to come] |
| Implantation | Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo |
| Hemocompatibility | Under development in the USP monograph Sterile Single-Use Plastic Large-Volume Containers for Human Blood and Blood Components |
| Chronic toxicity | [to come] |
| Carcinogenicity | [to come] |
| Reproductive or developmental toxicity | [to come] |
| Biodegradation | [to come] |
|
*
Additional general chapters referring to this biological effect include Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices
|
|
|
†
Additional general chapters referring to this biological effect include Injections
|
|
DRUG CONTAINERS
Biocompatibility of Plastic and Other Polymeric Drug Containers
Pharmaceutical containers consist of a container and a closure. Plastic containers may consist of polymers that upon extraction do not alter the stability of the contained product or do not exhibit toxicity. The biocompatibility testing requirements for drug containers are stated under Injections  1
1 and Containers—Plastics
and Containers—Plastics  661
661 . As directed in these chapters, the plastic or other polymeric portions of these products are tested according to the procedures set forth under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
. As directed in these chapters, the plastic or other polymeric portions of these products are tested according to the procedures set forth under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 . A plastic or other polymer that does not meet the requirements of Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
. A plastic or other polymer that does not meet the requirements of Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 is not a suitable material for a drug container. Materials that meet the in vitro requirements qualify as biocompatible materials without the need for further testing and may be used in the construction of a drug container. If a class designation (classes I–VI) for plastics or other polymers is desired, the appropriate testing procedures are performed as discussed in the section In Vivo Testing and Class Designation.
is not a suitable material for a drug container. Materials that meet the in vitro requirements qualify as biocompatible materials without the need for further testing and may be used in the construction of a drug container. If a class designation (classes I–VI) for plastics or other polymers is desired, the appropriate testing procedures are performed as discussed in the section In Vivo Testing and Class Designation.
Elastomeric Closures
Elastomeric closures are closures that can be pierced by a syringe and maintain their integrity because of their elastic properties. Elastomeric materials may be composed of several chemical entities including fillers, pigments, plasticizers, stabilizers, accelerators, vulcanizing agents, and a natural or a synthetic polymer. These materials are used for manufacturing a product with the desired elastomeric physical properties, and they frequently demonstrate biological reactivity—cellular degeneration and malformation—when tested with in vitro cell cultures.
The biocompatibility of an elastomeric material is evaluated according to the two-stage testing protocol specified in the Biological Test Procedures under Elastomeric Closures for Injections  381
381 . Unlike plastics or other polymers, an elastomeric material that does not meet the requirements of the first-stage (in vitro) testing may qualify as a biocompatible material by passing the second-stage (in vivo) testing, which consists of the Systemic Injection Test and the Intracutaneous Test described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
. Unlike plastics or other polymers, an elastomeric material that does not meet the requirements of the first-stage (in vitro) testing may qualify as a biocompatible material by passing the second-stage (in vivo) testing, which consists of the Systemic Injection Test and the Intracutaneous Test described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 . No class or type distinction is made between elastomeric materials that meet the requirements of the first stage of testing and those that qualify as biocompatible materials by meeting the second-stage requirements. Elastomeric materials are not assigned class I–VI designation.
. No class or type distinction is made between elastomeric materials that meet the requirements of the first stage of testing and those that qualify as biocompatible materials by meeting the second-stage requirements. Elastomeric materials are not assigned class I–VI designation.
MEDICAL DEVICES AND IMPLANTS
Medical devices and implants, labeled nonpyrogenic, in direct or indirect contact with the cardiovascular system or other soft body tissues, meet the requirements described under Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices  161
161 . The products listed in this chapter that meet the criteria are solution administration sets, extension sets, transfer sets, blood administration sets, intravenous catheters, dialyzers and dialysis tubing and accessories, transfusion and infusion assemblies, and intramuscular drug delivery catheters. The outlined criteria do not apply to medical products such as orthopedic products, latex gloves, and wound dressings.
. The products listed in this chapter that meet the criteria are solution administration sets, extension sets, transfer sets, blood administration sets, intravenous catheters, dialyzers and dialysis tubing and accessories, transfusion and infusion assemblies, and intramuscular drug delivery catheters. The outlined criteria do not apply to medical products such as orthopedic products, latex gloves, and wound dressings.
The testing requirements described or referenced under Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices  161
161 include Sterility, Bacterial endotoxins, Pyrogen, and Other requirements. A procedure to evaluate the presence of bacterial endotoxins is set forth under Bacterial Endotoxins Test
include Sterility, Bacterial endotoxins, Pyrogen, and Other requirements. A procedure to evaluate the presence of bacterial endotoxins is set forth under Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 , and the limits are set in Bacterial Endotoxins under Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices
, and the limits are set in Bacterial Endotoxins under Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices  161
161 . For devices that cannot be tested by the Bacterial Endotoxins Test
. For devices that cannot be tested by the Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 because of nonremovable inhibition or enhancement, the Pyrogen Test
because of nonremovable inhibition or enhancement, the Pyrogen Test  151
151 is applied. The procedures for evaluating medical devices purported to contain sterile pathways are set forth in Sterile Devices under Sterility Tests
is applied. The procedures for evaluating medical devices purported to contain sterile pathways are set forth in Sterile Devices under Sterility Tests  71
71 . A procedure for evaluating the safety of medical devices is set forth in the Safety Test under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
. A procedure for evaluating the safety of medical devices is set forth in the Safety Test under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 .
.
The plastic or other polymer components of medical devices meet the requirements specified for plastics and other polymers under Containers—Plastics  661
661 ; those made of elastomers meet the requirements under Elastomeric Closures for Injections
; those made of elastomers meet the requirements under Elastomeric Closures for Injections  381
381 . As directed in these chapters, the biocompatibility of the plastic, other polymeric, and elastomeric portions of these products are tested according to the procedures described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
. As directed in these chapters, the biocompatibility of the plastic, other polymeric, and elastomeric portions of these products are tested according to the procedures described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 . If a class designation for a plastic or other polymer is also required, the appropriate testing procedures described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
. If a class designation for a plastic or other polymer is also required, the appropriate testing procedures described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 are performed.
are performed.
As required for elastomeric closures, elastomeric materials that do not meet the in vitro requirements may qualify as biocompatible materials and may be used in the construction of medical devices if they meet the requirements of the Systemic Injection Test and the Intracutaneous Test under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 . As required for drug containers, plastics and other polymers that do not meet the in vitro testing requirements are not suitable materials for use in medical devices.
. As required for drug containers, plastics and other polymers that do not meet the in vitro testing requirements are not suitable materials for use in medical devices.
IN VITRO TESTING, IN VIVO TESTING, AND CLASS DESIGNATION FOR PLASTICS AND OTHER POLYMERS
The testing requirements specified under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 and Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
and Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 are designed to determine the biological reactivity of mammalian cell cultures and the biological response of animals to elastomeric, plastic, and other polymer materials with direct or indirect patient contact. The biological reactivity of these materials may depend on both their surface characteristics and their extractable chemical components. The testing procedures set forth in these chapters can often be performed with the material or an extract of the material under test, unless otherwise specified.
are designed to determine the biological reactivity of mammalian cell cultures and the biological response of animals to elastomeric, plastic, and other polymer materials with direct or indirect patient contact. The biological reactivity of these materials may depend on both their surface characteristics and their extractable chemical components. The testing procedures set forth in these chapters can often be performed with the material or an extract of the material under test, unless otherwise specified.
Preparation of Extracts
Evaluation of the biocompatibility of a whole medical product is often not realistic; thus, the use of representative portions or extracts of selected materials may be the only practical alternative for performing the assays. When representative portions of the materials or extracts of the materials under test are used, it is important to consider that raw materials may undergo chemical changes during the manufacturing, processing, and sterilization of a medical product. Although in vitro testing of raw materials can serve as an important screening procedure, a final evaluation of the biocompatibility of a medical product is performed with portions of the finished and sterilized product.
The preparation of extracts is performed according to the procedures set forth under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 and under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
and under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 . Extractions may be performed at various temperatures (121
. Extractions may be performed at various temperatures (121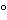 , 70
, 70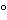 , 50
, 50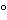 , or 37
, or 37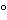 ), for various time intervals (1 hour, 24 hours, or 72 hours), and in different extraction media. The choice of extraction medium for the procedures under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
), for various time intervals (1 hour, 24 hours, or 72 hours), and in different extraction media. The choice of extraction medium for the procedures under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 includes Sodium Chloride Injection (0.9% NaCl) or tissue culture medium with or without serum. When medium with serum is used, the extraction temperature cannot exceed 37
includes Sodium Chloride Injection (0.9% NaCl) or tissue culture medium with or without serum. When medium with serum is used, the extraction temperature cannot exceed 37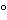 . In vivo extraction medium includes the choices described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
. In vivo extraction medium includes the choices described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 or the solvent to which the drug or medical device is exposed.
or the solvent to which the drug or medical device is exposed.
When choosing extraction conditions, select the temperature, solvent, and time variables that best mimic the “in use” conditions of the product. The performance of multiple tests at various conditions can be used to simulate variations in the “in use” conditions. Although careful selection of extraction conditions allows the simulation of manufacturing and processing conditions in the testing of raw materials, an evaluation of the biocompatibility of the product is performed with the finished and sterilized product.
In Vitro Testing
The procedures described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 include an Agar Diffusion Test (indirect contact test), a Direct Contact Test, and an Elution Test (extraction test). The sample is biocompatible if the cell cultures do not exhibit greater than a mild reactivity (Grade 2) to the material under test, as described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
include an Agar Diffusion Test (indirect contact test), a Direct Contact Test, and an Elution Test (extraction test). The sample is biocompatible if the cell cultures do not exhibit greater than a mild reactivity (Grade 2) to the material under test, as described under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 . The Agar Diffusion Test is designed to evaluate the biocompatibility of elastomeric materials. The material is placed on the agar overlay of the cell monolayer, which cushions the cells from physical damage by the material and allows leachable chemicals or materials to diffuse from the elastomer and contact the cell monolayer. Extracts of elastomeric materials are tested by placing the filter paper saturated with an extract of the elastomer on the solidified surface of the agar. The Direct Contact Test is designed for elastomeric or plastic materials that will not physically damage cells with which they are in direct contact. Any leachable chemicals diffuse from the material into the serum-supplemented growth medium and directly contact the cell monolayer. The Elution Test is designed to evaluate the extracts of polymeric materials. The material may be applied directly to the tissue culture media.
. The Agar Diffusion Test is designed to evaluate the biocompatibility of elastomeric materials. The material is placed on the agar overlay of the cell monolayer, which cushions the cells from physical damage by the material and allows leachable chemicals or materials to diffuse from the elastomer and contact the cell monolayer. Extracts of elastomeric materials are tested by placing the filter paper saturated with an extract of the elastomer on the solidified surface of the agar. The Direct Contact Test is designed for elastomeric or plastic materials that will not physically damage cells with which they are in direct contact. Any leachable chemicals diffuse from the material into the serum-supplemented growth medium and directly contact the cell monolayer. The Elution Test is designed to evaluate the extracts of polymeric materials. The material may be applied directly to the tissue culture media.
The performance of either the Agar Diffusion Test or the Direct Contact Test in combination with the Elution Test is the preferred testing protocol. Extraction of the product or materials for the Agar Diffusion Test or the Elution Test is performed as described in the Preparation of Extracts.
In Vivo Testing and Class Designation
According to the injection and implantation requirements specified in Table 1 under Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 , plastics and other polymers are assigned a class designation between class I and class VI. To obtain a plastic or other polymer class designation, extracts of the test material are produced according to the specified procedures in various media. To evaluate biocompatibility, the extracts are injected systemically and intracutaneously into mice and rabbits. According to the specified injection requirements, a plastic or other polymer may initially be graded as class I, II, III, or V. If in addition to injection testing, implantation testing using the material itself is performed, the plastic or other polymer may be classified as class IV or class VI.
, plastics and other polymers are assigned a class designation between class I and class VI. To obtain a plastic or other polymer class designation, extracts of the test material are produced according to the specified procedures in various media. To evaluate biocompatibility, the extracts are injected systemically and intracutaneously into mice and rabbits. According to the specified injection requirements, a plastic or other polymer may initially be graded as class I, II, III, or V. If in addition to injection testing, implantation testing using the material itself is performed, the plastic or other polymer may be classified as class IV or class VI.
BIOCOMPATIBILITY OF MEDICAL DEVICES AND IMPLANTS
In addition to evaluating medical products for compendial purposes according to the procedures specified under Injections  1
1 , Sterility
, Sterility  71
71 , Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro
, Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vitro  87
87 , Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo
, Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 , Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices
, Transfusion and Infusion Assemblies and Similar Medical Devices  161
161 , Elastomeric Closures for Injections
, Elastomeric Closures for Injections  381
381 , and Containers—Plastics
, and Containers—Plastics  661
661 , medical devices and implants are evaluated for sensitization, subchronic toxicity, genotoxicity, hemocompatibility, chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive or developmental toxicity, and biodegradation as required by the regulatory agencies.
, medical devices and implants are evaluated for sensitization, subchronic toxicity, genotoxicity, hemocompatibility, chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive or developmental toxicity, and biodegradation as required by the regulatory agencies.
The guidance provided by the regulatory agencies indicates that the extent of testing that is performed for a medical device or an implant depends on the following factors: (1) the similarity and uniqueness of the product relative to previously marketed (“predicate”) products as considered in the Decision Flowchart; (2) the extent and duration of the contact between the product and the patient as described in the Categorization of Medical Devices; and (3) the material composition of the product as considered in the sections Decision Flowchart and In Vivo Testing and Class Designation.
Decision Flowchart
as adapted from the FDA's Blue Book Memorandum #G95-1. The purpose of the flowchart is to determine whether the available data from previously marketed devices are sufficient to ensure the safety of the device under consideration. As indicated by the flowchart, the material composition and the manufacturing techniques of a product are compared to those of the previously marketed products for the devices that come in direct contact with the body. In addition, the flowchart requires an evaluation of the toxicity of any unique material that has not been used in predicate devices. Responses to the questions posed in the flowchart lead to the conclusion that either the available data are sufficient or additional testing is required to ensure the safety of the product. When additional testing is required, guidance on the identification of appropriate testing procedures is provided in the section Test Selection Matrix.
Categorization of Medical Devices
To facilitate the identification of appropriate testing procedures, medical devices are divided and subdivided, as shown in Table 2,
Table 2. Classification and Examples of Medical Devices
| Device Category | Device Subcategory | Nature or Extent of Contact | Some Examples |
| Skin | Devices that contact intact skin surfaces only | Electrodes, external prostheses, fixation tapes, compression bandages, and monitors of various types | |
| Surface Devices | Mucosal Membrane | Devices communicating with intact mucosal membranes |
Contact lenses, urinary catheters, intravaginal and intraintestinal devices (stomach tubes, sigmoidoscopes, colonoscopes, gas troscopes), endotracheal tubes, bronchoscopes, dental prostheses, orthodontic devices, and intrauterine devices |
| Breached or Compromised Surfaces | Devices that contact breached or otherwise compromised body surfaces | Ulcer, burn, and granulation tissue dressings or healing devices and occlusive patches | |
| Blood Path, Indirect | Devices that contact the blood path at one point and serve as a conduit for entry into the vascular system | Solution administration sets, extension sets, transfer sets, and blood administration sets | |
| External Communicating Devices |
Tissue, Bone, or Dentin Communicating | Devices and materials communicating with tissue, bone, or pulp and dentin system | Laparoscopes, arthroscopes, draining systems, dental cements, dental filling materials, and skin staples |
| Circulating blood | Devices that contact circulating blood | Intravascular catheters, temporary pacemaker electrodes, oxygenators, extracorporeal oxygenator tubing and accessories, dialyzers, dialysis tubing and accessories, hemoadsorbents, and immunoadsorbents | |
| Implant Devices | Tissue or Bone | Devices principally contacting bone or principally contacting tissue and tissue fluid | Examples of the former are orthopedic pins, plates, replacement joints, bone prostheses, cements, and intraosseous devices; examples of the latter are pacemakers, drug supply devices, neuromuscular sensors and simulators, replacement tendons, breast implants, artificial larynxes, subperiosteal implants, and ligation clips |
| Blood | Devices principally contacting blood | Pacemaker electrodes, artificial arteriovenous fistulae, heart valves, vascular grafts, internal drug delivery catheters, and ventricular-assist devices |
according to the nature and extent of their contact with the body. Major categories of medical devices are surface devices, external communicating devices, and implant devices. These are then further subcategorized. Some examples of medical devices and implants belonging to each of the subcategories are also presented in Table 2.
Test Selection Matrix
The matrix provides guidance on the identification of appropriate biological testing procedures for the three categories of medical devices: tests for Surface Devices (see Table 3), tests for External Communicating Devices (see Table 4), and tests for Implant Devices (see Table 5). Each category of devices is subcategorized and then even further subdivided according to the duration of the contact between the device and the body. The duration of contact is defined as (A) limited (less than 24 hours); (B) prolonged (24 hours to 30 days); or (C) permanent (more than 30 days). The biological effects that are included in the matrix are cytotoxicity, sensitization, irritation or intracutaneous reactivity, systemic toxicity, subchronic toxicity, genotoxicity, implantation, hemocompatibility, chronic toxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive or developmental toxicity, and biodegradation. The general chapters that contain toxicity testing procedure for these biological effects are indicated in Table 1.
Each subcategory in the matrix has an associated panel of testing requirements. Generally, the number of tests in the panel increases as the duration of the contact between the device and the body is extended and as the device or implant comes in closer contact with the circulatory system. Within several subcategories, the option of performing additional tests beyond those required should be considered on a case-by-case basis. Specific situations such as use of permanent implant devices or external communicating devices for pregnant women have to be taken into consideration in the manufacturer's decision to include reproductive or developmental testing. Guidance on the identification of possible additional testing procedures is provided in the matrix for each subcategory of medical devices.
GUIDANCE IN SELECTING THE PLASTIC OR OTHER POLYMER CLASS DESIGNATION FOR A MEDICAL DEVICE
To provide guidance on selecting the appropriate plastic or other polymer class designation for a medical device, each subcategory of Surface Devices (see Figure 2)
Fig. 2. USP plastic and other polymer class requirements for surface devices.* Categorization based on duration of contact: limited—less than 24 hours; prolonged—24 hours to 30 days; permanent—more than 30 days.† USP Plastic Class designation.
and External Communicating Devices (see Figure 3)
Fig. 3. USP plastic and other polymer class requirements for external communicating devices. * Categorization based on duration of contact: limited—less than 24 hours; prolonged—24 hours to 30 days; permanent—more than 30 days.† USP Plastic Class designation.
is assigned a USP Plastic Class designation (see Biological Reactivity Tests, In Vivo  88
88 ). If the tests for each USP class designation are not sufficient for a specific device, the manufacturer or the practitioner must develop an appropriate set of tests. The indicated numerical class number increases relative to the duration (risk) of contact between the device and the body. In the category of Implant Devices, the exclusive use of class VI is mandatory. The assignment of USP Plastic Class designation is based on the test selection matrices illustrated in Tables 3, 4, and 5.
). If the tests for each USP class designation are not sufficient for a specific device, the manufacturer or the practitioner must develop an appropriate set of tests. The indicated numerical class number increases relative to the duration (risk) of contact between the device and the body. In the category of Implant Devices, the exclusive use of class VI is mandatory. The assignment of USP Plastic Class designation is based on the test selection matrices illustrated in Tables 3, 4, and 5.
The assignment of a plastic or other polymer class designation to a subcategory is not intended to restrict the use of higher classes of plastics or other polymers. Although the assigned class defines the lowest numerical class of plastic or other polymer that may be used in the corresponding device, the use of a numerically higher class of plastic is optional. When a device can be defined as belonging to more than one device category, the plastic or other polymer should meet the requirements of the highest numerical class.
Table 3. Test Selection Matrix for Surface Devices.*
| Device Categories | Biological Effectb | |||||||||||||
| Body Contact | Contact Durationa | Cytotoxicity | Sensitization | Irritation or Intracutaneous Reactivity | Systemic Toxicity (Acute) | Subchronic Toxicity (Subacute) | Genotoxicity | Implantation | Hemocompatability | Chronic Toxicity | Carcinogenicity | Reproductive or Development Toxicity | Biodegra- dation |
|
| A | X | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| Skin | B | X | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| C | X | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| Surface Devices |
Mucosal Membrane |
A | X | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| B | X | X | X | O | O | — | O | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| C | X | X | X | O | X | X | O | — | O | — | — | — | ||
| Breached or Compromised Surfaces |
A | X | X | X | O | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| B | X | X | X | O | O | — | O | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| C | X | X | X | O | X | X | O | — | O | — | — | — | ||
|
a
Legend A—limited (less than 24 hours); B—prolonged (24 hours to 30 days); C—permanent (more than 30 days).
|
||||||||||||||
|
b
Legend X—ISO evaluation tests for consideration; O—additional tests that may be applicable.
|
||||||||||||||
|
*
Adapted from the FDA's Blue Book Memorandum #G95-1 (Table 1. Initial Evaluation Tests for Consideration and Table 2. Supplementary Evaluation Tests for Consideration).
|
||||||||||||||
Table 4. Test Selection Matrix for External Communicating Devices.*
| Device Categories | Biological Effectb | |||||||||||||
| Body Contact | Contact Durationa | Cytotoxicity | Sensitization | Irritation or Intracutaneous Reactivity | Systemic Toxicity (Acute) | Subchronic Toxicity (Subacute) | Genotoxicity | Implantation | Hemocompatability | Chronic Toxicity | Carcinogenicity | Reproductive or Development Toxicity | Biodegra- dation |
|
| Blood Path, Indirect |
A | X | X | X | X | — | — | — | X | — | — | — | — | |
| B | X | X | X | X | O | — | — | X | — | — | — | — | ||
| C | X | X | O | X | X | X | O | X | X | X | — | — | ||
| External Communicating Devices |
Tissue, Bone, or Dentin Communi- cating |
A | X | X | X | O | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| B | X | X | O | O | O | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| C | X | X | O | O | O | X | X | — | X | X | — | — | ||
| Circulating Blood |
A | X | X | X | X | — | O | — | X | — | — | — | — | |
| B | X | X | X | X | O | X | O | X | — | — | — | — | ||
| C | X | X | X | X | X | X | O | X | X | X | — | — | ||
|
a
Legend A—limited (less than 24 hours); B—prolonged (24 hours to 30 days); C—permanent (more than 30 days).
|
||||||||||||||
|
b
Legend X—ISO evaluation tests for consideration; O—additional tests that may be applicable.
|
||||||||||||||
|
*
Adapted from the FDA's Blue Book Memorandum #G95-1 (Table 1. Initial Evaluation Tests for Consideration and Table 2. Supplementary Evaluation Tests for Consideration).
|
||||||||||||||
Table 5. Test Selection Matrix for Implant Devices.*
| Device Categories | Biological Effectb | |||||||||||||
| Body Contact | Contact Durationa | Cytotoxicity | Sensitization | Irritation or Intracutaneous Reactivity | Systemic Toxicity (Acute) | Subchronic Toxicity (Subacute) | Genotoxicity | Implantation | Hemocompatibility | Chronic Toxicity | Carcinogenicity | Reproductive or Development Toxicity | Biodegra- dation |
|
| A | X | X | X | O | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||
| Tissue or Bone |
B | X | X | O | O | O | X | X | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Implant Devices |
C | X | X | O | O | O | X | X | — | X | X | — | — | |
| A | X | X | X | X | — | — | X | X | — | — | — | — | ||
| Blood | B | X | X | X | X | O | X | X | X | — | — | — | — | |
| C | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | — | — | ||
|
a
Legend A—limited (less than 24 hours); B—prolonged (24 hours to 30 days); C—permanent (more than 30 days).
|
||||||||||||||
|
b
Legend X—ISO evaluation tests for consideration; O—additional tests that may be applicable.
|
||||||||||||||
|
*
Adapted from the FDA's Blue Book Memorandum #G95-1 (Table 1. Initial Evaluation Tests for Consideration and Table 2. Supplementary Evaluation Tests for Consideration).
|
||||||||||||||
1
ISO document 10993-1:1997 entitled Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 1: Evaluation and Testing.
*
Adapted from the FDA Blue Book Memorandum #G95-1 (“Use of International Standard ISO-10993.‘Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices-Part 1: Evaluation and Testing.’”)
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| General Chapter | Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(GTMDB05) General Toxicology and Medical Device Biocompatibility |
USP32–NF27 Page 408


